Exploration
Five Priceless Shipwrecks in US Waters
Metal detecting maven Alex Lemaire explores five of the most precious wrecks discovered off the American coasts.

by Alex Lemaire
Shipwrecks are windows into the past. They help us learn more about history. And with an estimated three million shipwrecks around the world, most of them yet to be discovered, there awaits an amazing adventure for the intrepid explorer yearning to know more. Some of these shipwrecks are special because of their historical significance or because of the valuable cargo they carried. Here are brief sketches of five of the most precious shipwrecks discovered in American waters.
SS Central America Shipwreck

One such shipwreck happened during the California gold rush. The sidewheel steamer, SS Central America, loaded with 30,000 pounds/13.6 metric tons of gold, was sunk by a hurricane in September 1857 off the coast of South Carolina. The sails were shredded by the winds, and the boiler failed. The crew and passengers formed a bucket brigade and valiantly tried to keep the ship afloat, but their efforts were in vain. The Central America sank, killing 425 or the 578 passengers aboard.
After 130 years, the famous treasure hunter, Tommy Thompson, discovered the wreck at 2200 m/7200 ft of water. In an operation that lasted four years, Thompson, using a remotely-operated vehicle, recovered the gold—gold bars, freshly minted coins, gold dust, along with other valuable items totaling $2,000,000 then, and $54,000,000 today.
H. L. Hunley
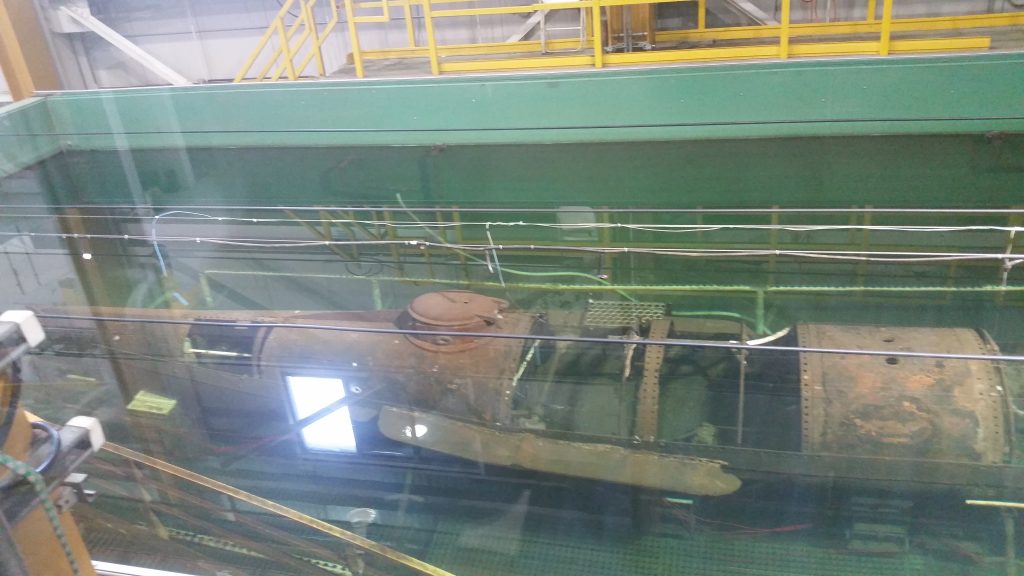

The H. L. Hunley, historically the first submarine to successfully sink an enemy ship, was launched in July 1863 during the Civil War. The Hunley measured around 37 feet long and was designed for a crew of nine, eight of which turned a hand-cranked propeller while the ninth man steered. Built in Alabama then shipped by train to Charleston, South Carolina, she was used by the Confederates in their attack of Union ships attempting to break through the naval blockade.
Hunley sank on February 17, 1864, after torpedoing and sinking the warship USS Housatonic. She disappeared for over a century until Edward Lee Spence, an underwater archeologist and the founder of the commercial diving school, the International Diving Institute, discovered and salvaged the wreck in 2000. She was found just four miles from Charleston Harbor and relocated by Spence to the Warren Lasch Conservation Center. The value of the discovery is estimated to be more than $40,000,000 dollars.
SS Republic Shipwreck

On October 25, 1865, The SS Republic wrecked 100 miles off the coast of Georgia at 520 m/1700 ft in the Atlantic seabed. The Republic is a sidewheel steamship that sank due to the devastating force of a violent hurricane, saving most of the passengers and crew, but losing its precious cargo of over $4,000,000 in silver and gold coins—much needed to rebuild New Orleans’s post-Civil War economy, and a fortune even in today’s money.
Nearly 140 years later, Odyssey Marine Exploration, a company specializing in locating and exploring shipwrecks, discovered the Republic using cutting-edge technologies, such as powerful sonars, magnetometers, and advanced robotics. A soft silicone limpet was used, having been specially designed to pick up one coin at a time without damaging its surface. The entire expedition was documented by National Geographic.
Whydah Gally
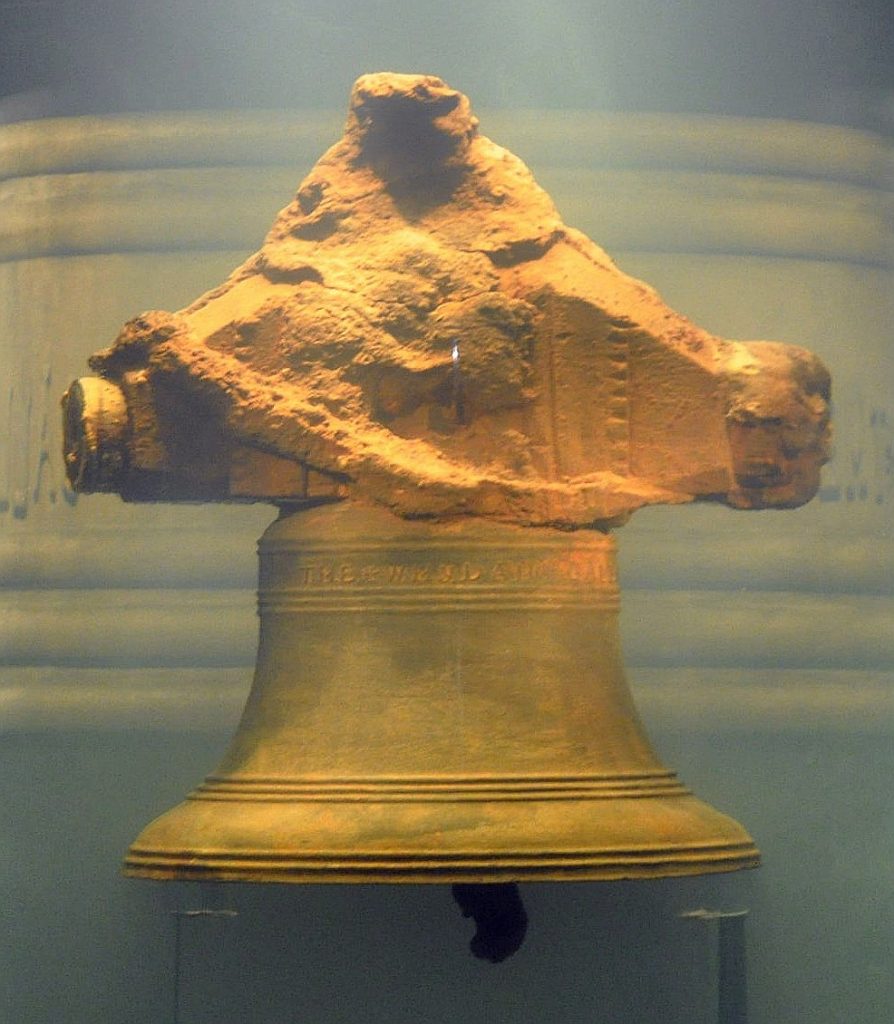
Whydah Gally is the only fully authenticated pirate shipwreck ever discovered in US waters, having been found by the underwater archaeologist Barry Clifford in 1984. The ship’s identity was verified a year later after the discovery of its bell, which was inscribed with the vessel’s name “THE WHYDAH GALLY 1716”.
The 100-ft-long ship was commissioned in 1715 and launched in 1716 in London. With a top speed of 13 knots, the Whydah was originally built to transport passengers, cargo, and slaves. But, in 1717, on the return leg of its maiden voyage of the triangle trade, it was captured by Samuel “Black Sam” Bellamy, who was one of the wealthiest pirates in history.
The pirate had modified and equipped Whydah Gally with ten additional cannons and sailed north. He used his newly acquired ship to loot and capture other vessels on the way. Months later, the ship was hit by a storm and sank off the coast of Massachusetts. Only two of the Whydah’s crew survived, along with seven others who were on a sloop captured by Bellamy earlier that day. Six of the nine survivors were hanged, two who had been forced into piracy were freed, and one Indian crewman was sold into slavery.

The Whydah eluded discovery for over 260 years, when it was found buried under 3 m/10 ft to 15 m/50 ft of sand in depths ranging from 5 m/16 ft to 9 m/30 ft, spread over four miles parallel to Cape Cod’s easternmost coast. The site has been extensively studied for many years. More than 200,000 individual pieces have been recovered. Some of them are displayed at Whydah Sea-Lab & Learning Center in Provincetown, Massachusetts.
Nuestra Senora de Atocha Shipwreck (Our Lady of Atocha)

The Spanish galleon, Nuestra Señora de Atocha, named after the parish of Atocha in Madrid, was the most widely known vessel of a fleet of ships. In 1622, she sank to the bottom of the Atlantic in a hurricane off the Florida Keys. At the time of her sinking, she was heavily laden with copper, silver, gold, tobacco, gems, and indigo bound for Spain. Emeralds from the Muzo Mine in Columbia, renowned as the world’s finest emeralds, were among the treasures.
After an expensive and arduous search that began in 1969 with Mel Fisher, an American treasure hunter, finding silver bars in 1973, a bronze cannon in 1975—proving to be that of the Atocha. Fisher lost his son, his daughter-in-law, and another diver while pursuing the treasure, but he persevered, finally finding the wreck and its treasure in 1985.
The State of Florida claimed title to the wreck but, after eight years of litigation, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in favor of Fisher’s company, which granted him rights to all found treasure in 1982. Fisher died in 1998. The ship’s cargo is estimated to be worth $400,000,000. In 2014, the Senora de Atocha was recognized by the Guinness Book of World Records as the most valuable shipwreck ever discovered. Some of the items are displayed at the Mel Fisher Maritime Museum in Key West, Florida.
This Spanish treasure galleon, and most widely known vessel of a fleet of ships, sank to the bottom of the Atlantic due to a hurricane in 1622. In 1985, it was discovered—loaded with 40 tons/36.2 m tons of gold and silver, plus 70 pounds/31.6 kg of emeralds—off the Florida Keys in 1985 by Mel Fisher, an American treasure hunter who died in 1998.
Finding this precious shipwreck wasn’t an easy task. Mel Fisher started looking for it in 1969. He spent a lot of money and effort to locate it. He lost his son, his daughter-in-law, and a diver during this expedition.
He didn’t give up, and he kept working. He found three silver bars in 1973 and five cannons in 1975. This convinced him that he was getting closer to the main hull. In July 1985, he made the great discovery. The ship’s cargo is estimated to be worth $400,000,000.
But this didn’t mean that the fight was over. He had to win a lengthy court battle against the State of Florida over the ownership of the gold. Some of the items are displayed at the Mel Fisher Maritime Museum in Key West. Three years later, Congress passed the Abandoned Shipwrecks Act. In 2014, the Senora de Atocha was recognized by the Guinness Book of World Records as the most valuable shipwreck ever discovered.

Alex Lemaire is passionate about treasure hunting whether inland or underwater. He published many articles about this subject on his blog. He thinks that this hobby is an amazing way to learn more about the history of humanity.