Community
What Was Life Like on the Mars? Cold Water Forensics with Explorer Richard Lundgren
This summer Richard Lundgren and his select team of the Mars veterans, aka Martians will return to the source to hopefully answer the question, “What was life really like for the 600-800 sailors on Mars The Magnificent, King Erik XIV’s warship, which was lost in battle and sank in 1564 in the Baltic Sea. Unfortunately, they don’t know where the bodies are buried, yet; that’s the focus of this summer’s research. We turned to Our Favorite Martian to bring us up to speed on the project and the state of their undersea forensics.
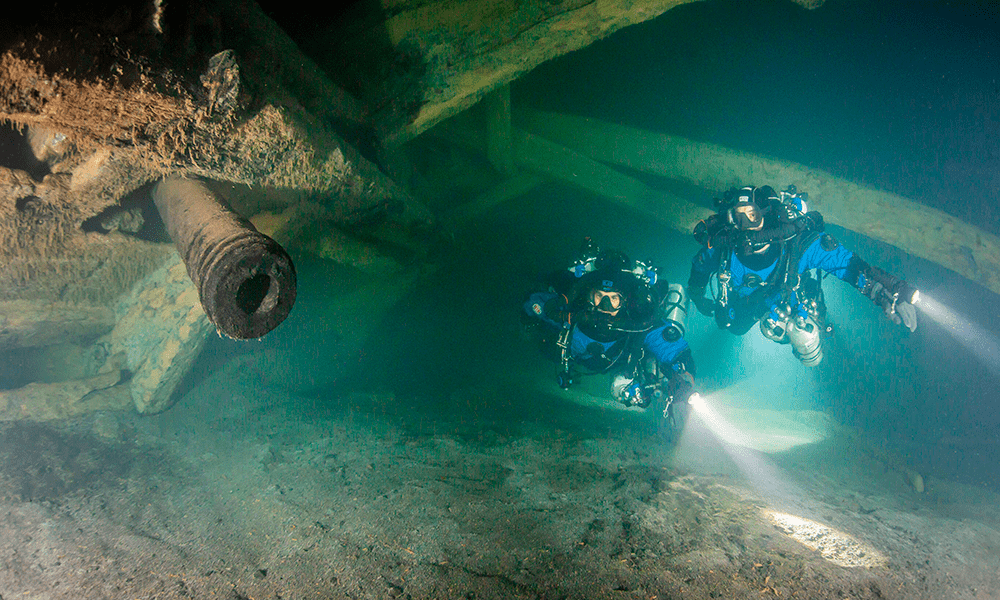
by Michael Menduno
Header Image: Kirill Egorov
Richard Lundgren is arguably one of the most prolific shipwreck explorers of our time. The 49-year old, ex-commercial diver, photographer & filmmaker, GUE instructor trainer, and expedition leader has discovered more than 120 shipwrecks in the Baltic Sea since the 1990s. He accomplished all this while fielding photographic assignments from the likes of National Geographic, the BBC, The History Channel, The Discovery Channel and others.
The Crowning Jewel? In May 2011, with his team from Ocean Discovery. Lundgren found Sweden’s most famous shipwreck—Mars the Magnificent—King Erik XIV’s warship, which had been lost in battle and sank in 1564 in the Southeast Baltic Sea. In finding The Mars, he fulfilled a vow that he made as a precocious eight-year old boy–one day he would “find the ship” after visiting the Vasa Museum in Stockholm.
Most of Lundgren’s time over the last eight years has been occupied with documenting and studying the wreck in cooperation with a number of government, academic, and scientific organizations. Their work included pioneering the use of photogrammetry and 3D modeling, which not only helps scientists, but also informs the public about the find.
We caught up with Lundgren as he and his veteran team of “Martians” were planning to further explore the wreck in hopes of answering the question: What was life like on Mars? Here’s what our favorite Martian had to say about the status of the project.
InDepth: How has the Mars documentary been received?
Lundgren: It’s had great success. It’s been shown in over 30 countries, and it’s showing on the Smithsonian channel in the U.S. It’s also available online in many languages, though its not on Netflix.
I know that your photomosaic treatment of the wreck also received broad coverage.
The photomosaic was on 64 magazine covers and the 3D model adds to this success.



OMG! That must be some sort of record. Weren’t you working on a 3D model of the wreck as well?
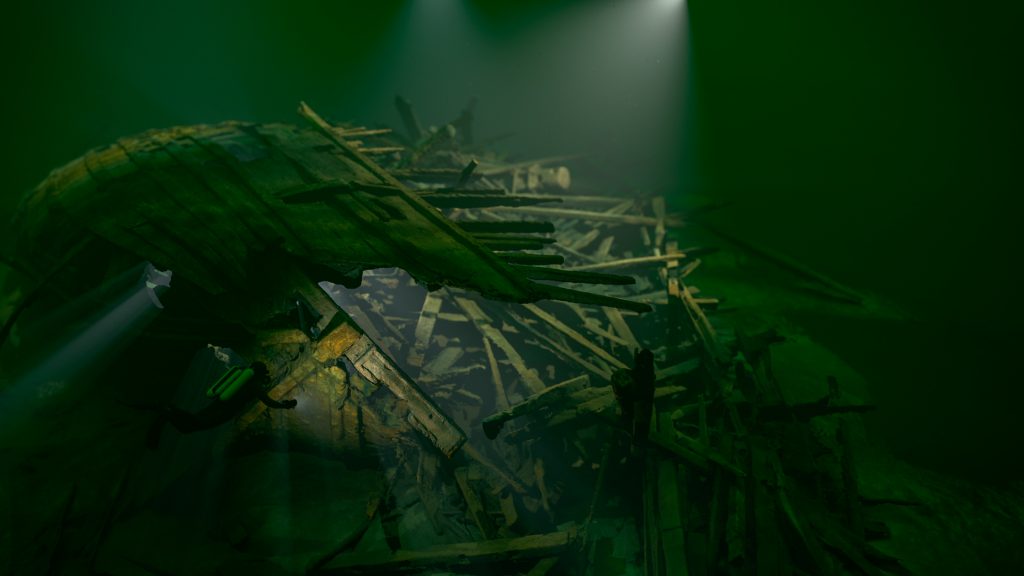
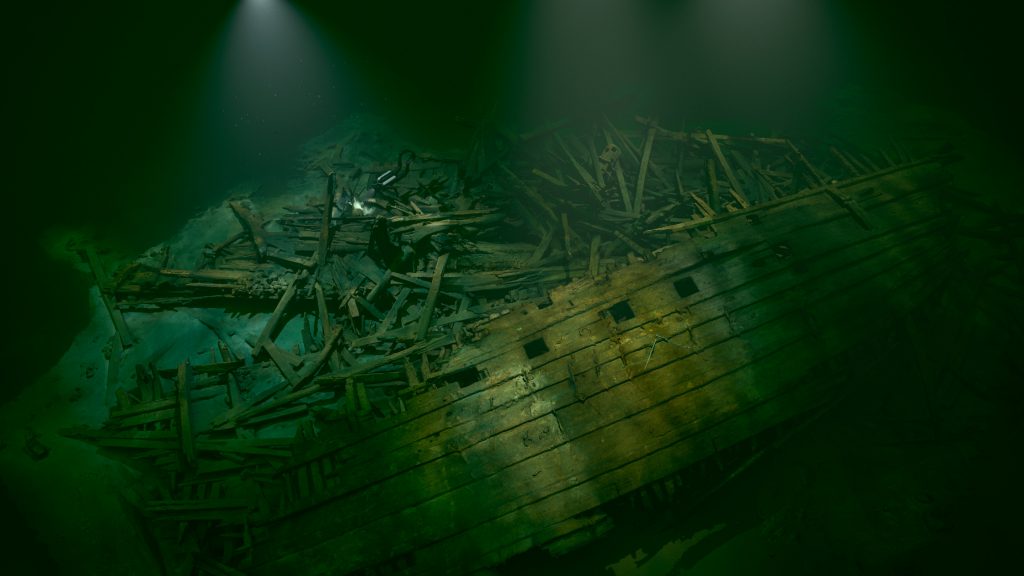
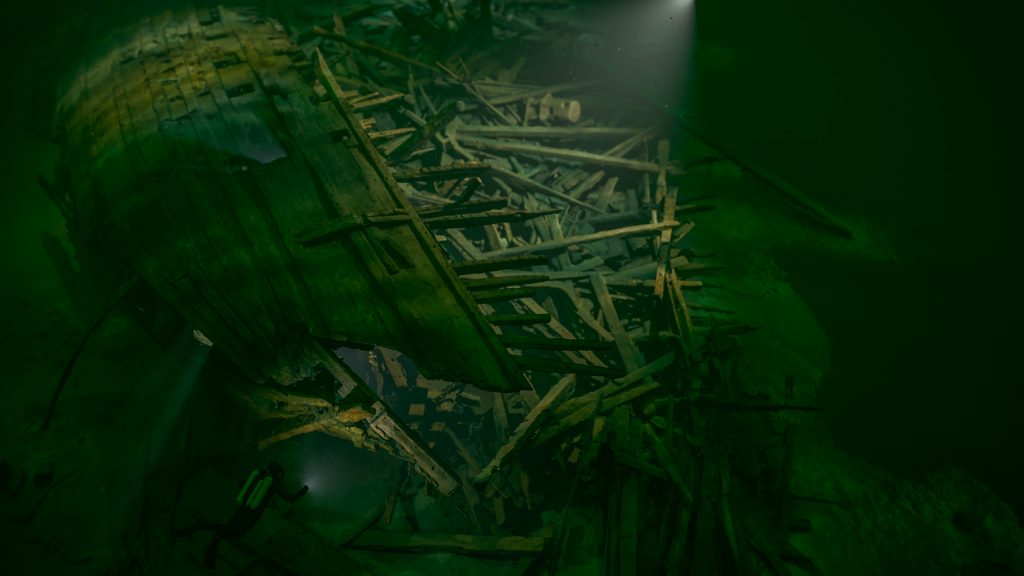
Yes, we received a grant from National Geographic Society/Waitt Grants Program to build a model which is now complete. One of the most advanced 3D model of a shipwreck ever. It was created from 30,000 images and is accurate to less than centimeters. In full resolution, you need a fantastic computer to see it all. We’re creating an entire website for it. We’ve also printed a scale model that is 1:25, 2 x 1.6 x 08 m, which is in the Västerviks Museum in Västervik, Sweden.
One of the most advanced 3D model of a shipwreck ever. It was created from 30,000 images and is accurate to less than centimeters.
I understand it was quite challenging to create.
We wanted to make a 3D model but didn’t want to make it using 2D images. We wanted to make scientifically correct. People told us that it was impossible to do. Of course, they said that about finding Mars as well. But that made it even more motivating for us.
How long did it take you?
It took us five years to take all the pictures and create the model. That part of the project was self-funded, so it took a lot of time. Now we have the problem that other outlets and channels are interested in the model. How can you price such a thing? How many trimix dives did it take to get 20-30k images? It’s almost funny now. They can bid for it, but what they are willing to pay only covers a few days of diving.
But the coolest thing is this. The Mars will be one of Facebook’s new Oculus Quest VR platform. That’s really going to be something!
Oculus Quest? That’s fantastic! How did that come about?
Well Mars is an incredible discovery, and we have focused on helping the public actually visualize the shipwreck. That has contributed to the huge interest. As a result, we got a call from the right person at Facebook who said that they wanted to recreate it as a virtual reality experience.
When is the virtual dive on the Mars scheduled to launch?
We’re hoping some time this summer. We’re currently testing an alpha unit.
Mars here we come! How many actual dives have you and you team conducted on the shipwreck so far?
On average we have had 12-14 divers diving the wreck for two weeks for seven years now. On average one diver performs 8 dives during these two weeks. Since 2011, we have only skipped one year. We did approximately 600 dives, all, I should note, without a single incident.
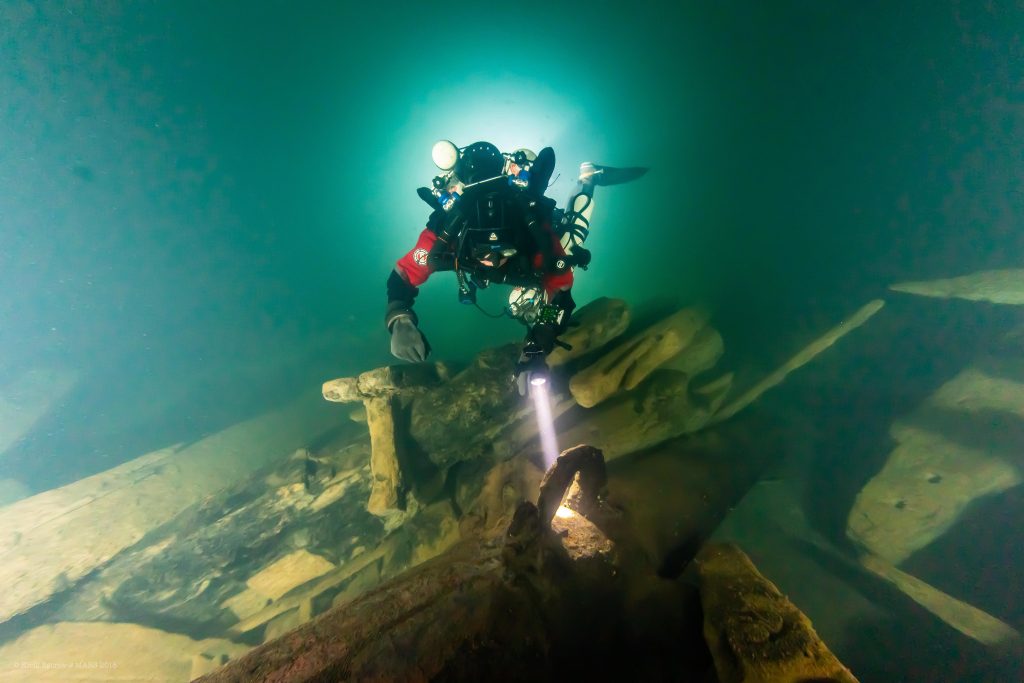

Wow. That’s a great safety record! Congratulations! So what are your next steps for Mars?
One of the most important things right now is the ongoing scientific project to understand life aboard Mars. That’s our main focus this summer. To do that we hope to find more bodies, and armour, and things like boarding nets. It’s a forensic study. We find some gruesome stuff. There should be 600+ bodies from Mars and 2-300 from the enemy ship as they were boarding the ship as it blew up. We have only found a few of them. Also, we haven’t figured out why the bodies aren’t spread out evenly throughout the shipwreck.
One of the most important things right now is the ongoing scientific project to understand life aboard Mars. That’s our main focus this summer. To do that we hope to find more bodies, and armour, and things like boarding nets. It’s a forensic study.
One speculation is that the boat surrendered before it blew up and sailors were gathered in one area. We’re hoping to find clues. I mean aliens haven’t taken them! We should find bones and skeletons, but we haven’t seen them yet. We have seen bone parts, but not skeletons. It’s odd because their bodies were in armor, and there was no one to take the bodies away. There is a very marginal bottom current. They should be there.
Fascinating! Wasn’t there another wreck involved as well?
Yes, we are also trying to find the Danish warship the Long Barque. Der Alte Bark in German, which Mars sank. We have a strong candidate that we found two years ago. It’s the right age but the wreck has not yet been confirmed. To my way of thinking, it’s one of the best-preserved shipwrecks I have ever seen. It sits upright on the bottom with two masts. We discovered the wreck on the northern tip of the Island of Oland. That’s part of our project this summer.
We plan to build a 3D model of the wreck using ROVs. We’ll scan the bottom and the wreck. We need something to identify her, like the inscriptions on the cannons on Mars. We’re still looking, but it’s pretty hard. The wreck has been underwater for five centuries. There were no ship bells back then with the ship’s name inscribed on them.
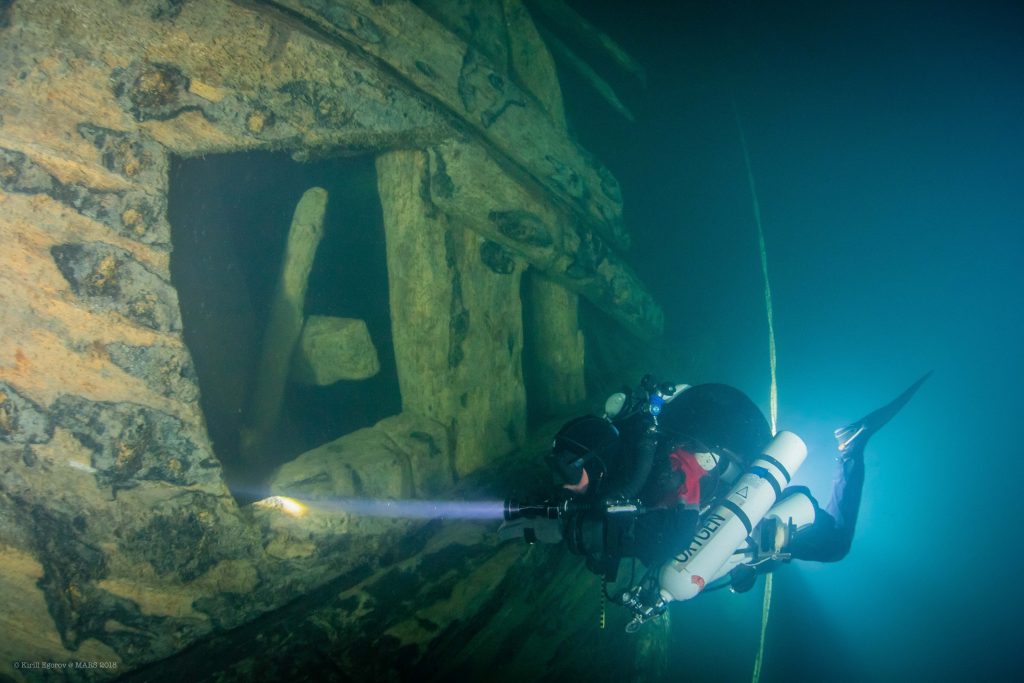

Who do you have working with you this summer?
They’re all Mars veterans. We call them Martians! They are all GUE divers. All are very experienced. We’re working with the Swedish Defense College, and MARIS is the scientific leader. We also have Professor Jon Adams on the team from the University of Southampton, who worked on the Mary Rose shipwreck. We’ll have graduate students and five to ten scientists present. It’s a cool interaction for the divers.
What is a typical dive profile?
The depth is 250 ft/76m on average. The water temperature is close to 2 C/36F. It’s a little warmer above 100 ft/30 m, like 10-15 C/50-59F, but that’s still fairly cold. We’re running 40-50 minute bottom times and then we’re “in the freezer” for 120-180 minutes. We investigated using a diving bell for decompression, but it was too complicated. We’re using full body electric heating and electric gloves from Santi. They’re super good. We also only do one dive a day. We leave early and we’re back by 2:00 pm. By 4-5 pm we hand over all the data.
I think it was explorer and engineer Dr. Bill Stone who said, “the difference between exploration and adventure is data.”
We’ve got the data brother!
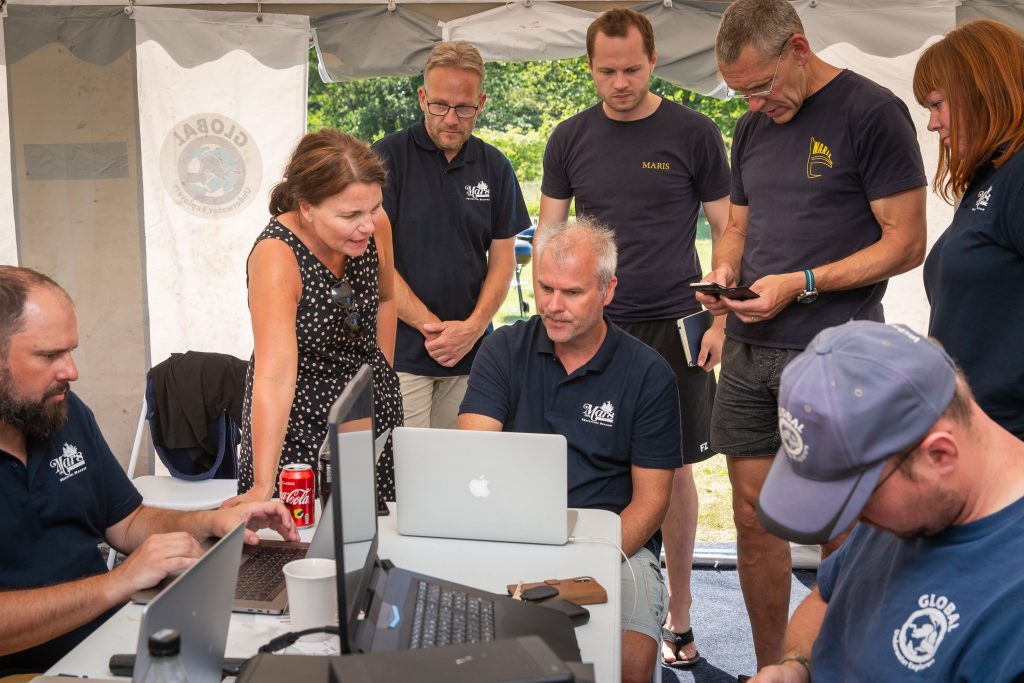

2019 Mars Team i.e. Martians: Johan Rönnby, Ingvar Sjöblom, Ingemar Lundgren, Kirill Egorov, Jesper Kjøller, Marco Al, Kees Beemster Leverenz, John Kendall ,Rachael Kendall, Oleksiy Sverdlov, Marcus New, Su Eun Kim, Kyungsoo Kim, Ellen Ingers, Joachim Ande,r Joakim Holmlund, Matilda Fredriksson, Rolf Warming, and Veronica Palm
Dive Deeper:
The Man From Mars, X-Ray Magazine, FEB 2014
Explore a 16th Century Underwater Battlefield, National Geographic Society
Archaeologists reveal new finds from legendary Swedish warship Science Nordic July 2018
MONSTER SHIPWRECK: MYSTERY OF THE MARS
The 1564 Maritime Battlefield of “Mars”
National Geographic Society Supports Exploration of Famed Swedish Warship Mars the Magnificent
Cursed Warship Revealed With Treasure Onboard
450-Years Old cursed warship yields treasure trove of artifacts
Schiffswrack “Mars”: Kampf um die Ostsee
Svenskt örlogsfartyg från 1500-talet avslöjar historiska hemligheter
National Geographic Society stödjer utforskning av svenskt krigsfartyg
Researchers explore cursed 450-year-old shipwreck at the bottom of the Baltic Sea
The Explorers Club Flag # 215: Mars the Magnificent with Richard Lundgren
The Explorer’s Club Flag #215 Report
Team to Complete Digital Reconstruction of Sunken Warship “Mars”
Related Stories:
EXPLORING THE BIKINI ATOLL’S USS SARATOGA
EXTENDING THE ENVELOPE REVISITED: CORRECTING THE RECORD OF THE 30 DEEPEST TECH SHIPWRECK DIVES

Michael Menduno is InDepth’s executive editor and, an award-winning reporter and technologist who has written about diving and diving technology for 30 years. He coined the term “technical diving.” His magazine “aquaCORPS: The Journal for Technical Diving”(1990-1996), helped usher tech diving into mainstream sports diving. He also produced the first Tek, EUROTek, and ASIATek conferences, and organized Rebreather Forums 1.0 and 2.0. Michael received the OZTEKMedia Excellence Award in 2011, the EUROTek Lifetime Achievement Award in 2012 and the TEKDive USA Media Award in 2018.